High blood pressure is the leading risk factor for stroke. It is also a risk factor for heart attacks and is linked to a number of heart conditions including heart failure and atrial fibrillation.
What is Blood Pressure?
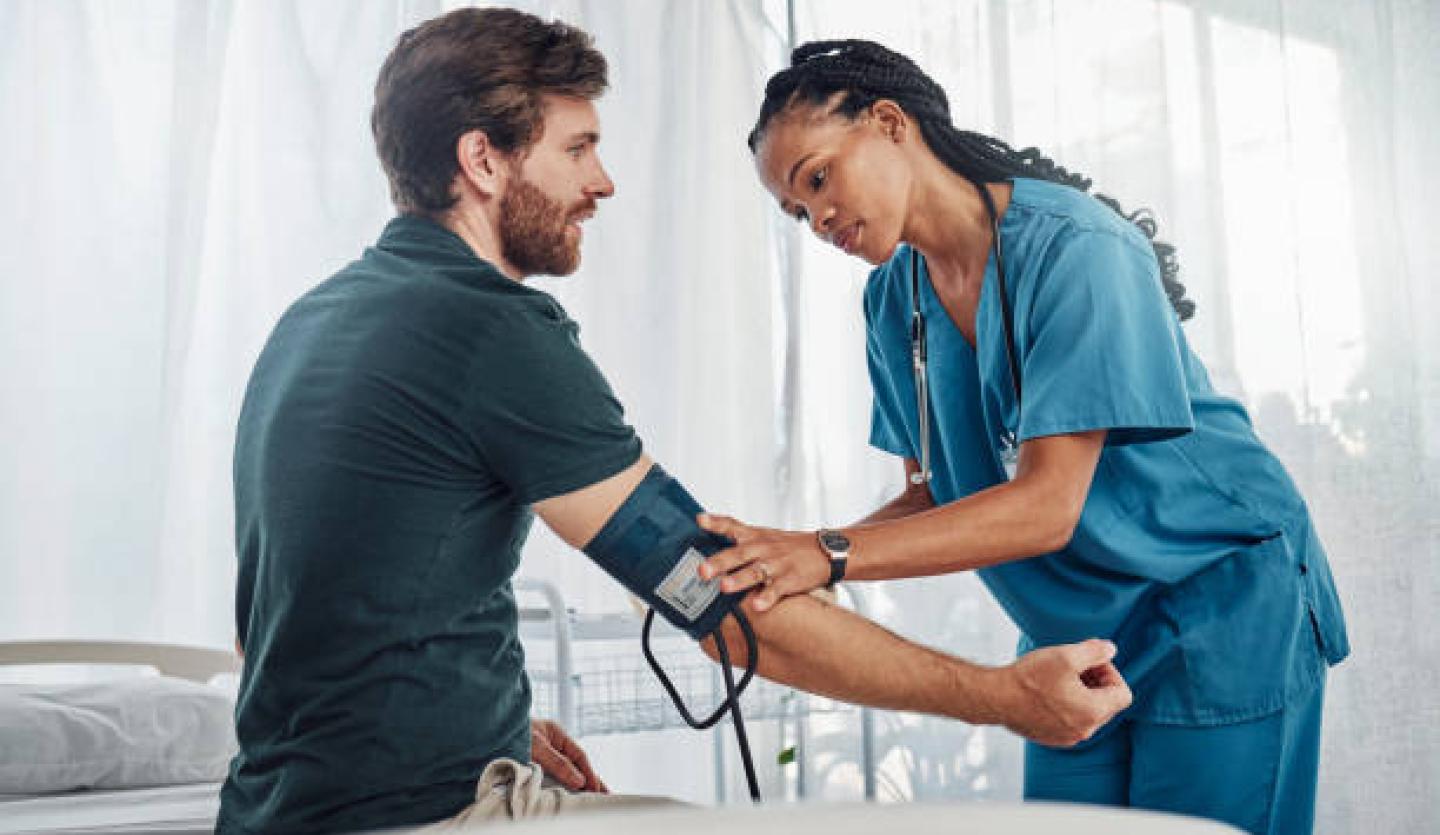
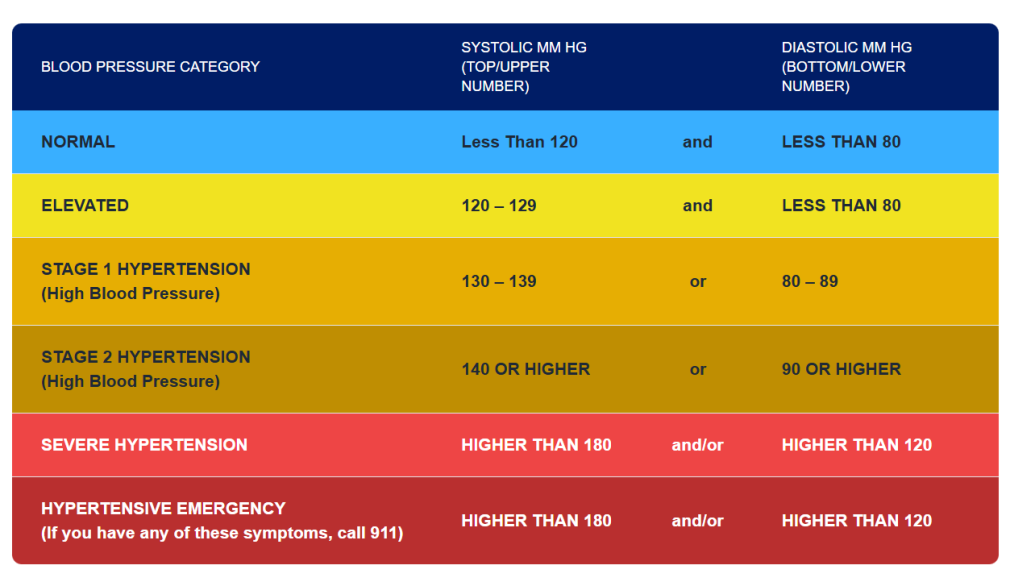
Blood pressure is the measured force of blood flowing through the body's vessels. This happens due to the heart pumping or contracting in response to electrical signals. Without this pressure, our body would be unable to deliver oxygen from our lungs to our vital organs. This force is expressed in two numbers:
- Systolic pressure—the top number
- Diastolic pressure—the bottom number
According to the American Heart Association, “High blood pressure (including stage 1 or stage 2 hypertension) affects nearly half of all adults in the US and is the leading cause of death in the US and around the world.”
Links to Serious Conditions beyond Heart Disease
In addition to cardiovascular problems, research now links high blood pressure to other serious health problems including cognitive decline, dementia, chronic kidney disease and pregnancy complications like pre-eclampsia.
As a result, the US has updated its national guidelines for diagnosing and treating high blood pressure. These new guidelines were developed by the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology (AHA/ACC) and replace the 2017 AHA/ACC guidelines.
They include new evidence, tools and strategies that focus on improving blood pressure control through accurate measurement, consistent treatment, healthy lifestyle behaviors and patient-focused care.
Updated Guidelines
The key emphasis for these new guidelines include prevention and early treatment to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and other serious conditions. Significant updates to the new 2025 guidelines include:
Use of the AHA PREVENT™ Risk Calculator: A new tool for estimating an individual’s risk of developing cardiovascular disease. This tool is also designed to help assess the risk for a broader range of potential health problems.
Additional Monitoring Recommendations: Regular blood pressure checks should be performed for all ages and include guidance on home monitoring.
Emphasis on Checking Blood Pressure before, during and after pregnancy to monitor, quickly treat, and reduce the risk of serious complications including preeclampsia.
Lifestyle and Nutrition Guidance: Reinforced recommendations for eating a healthy diet low in sodium, physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight and other lifestyle factors including reducing alcohol intake and managing stress.
Focus on Life’s Essential 8: The AHA has an updated checklist for maintaining cardiovascular health - now central to blood pressure management.
Updated Medication Guidance: In some cases, medication may be necessary for earlier treatment of high blood pressure.
Emergency Situation Awareness: Provide clearer information about the signs and symptoms of dangerously high blood pressure.